Reflective practice is the intentional process of analysing, evaluating, and learning from your own experiences, actions, and decisions.1
It’s about critically examining and thinking about what you did, why you did it, and what you learned.
Reflective practice is commonly used to develop learning, improve performance, and promote continuous growth.
Reflecting on the decisions you make during work is important to ensure you’re not always acting on instinct, but carefully considering your actions and their consequences.1
There isn’t always time to seek feedback or advice when you’re working with young people. Reflecting on your choices afterwards helps to ensure you’re always working in the best interest of the young person.1
It can also help promote self-care and prevent compassion fatigue and burnout, as it involves identifying challenges you might be facing and thinking about possible solutions.1
Self-awareness
You become more aware of your thoughts, emotions, and behaviours in various situations. This self-awareness helps you gain insight into your strengths, weaknesses, biases, and assumptions.
Critical thinking
You examine experiences from multiple perspectives, questioning assumptions, and considering alternative actions.
Develop ethical standards
You might analyse ethical dilemmas, considering what actions to take in a situation and how to make decisions in difficult or unclear situations.
Learning and improvement
Through reflection, individuals can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to enhance their skills and knowledge.
Problem-solving
By looking at past experiences, you can identify patterns, anticipate potential issues, and develop creative solutions. This will help you address challenges and solve problems more effectively.
Continuous growth
It encourages you to set goals, take actions, reflect on the outcomes, and adjust your approach as needed.
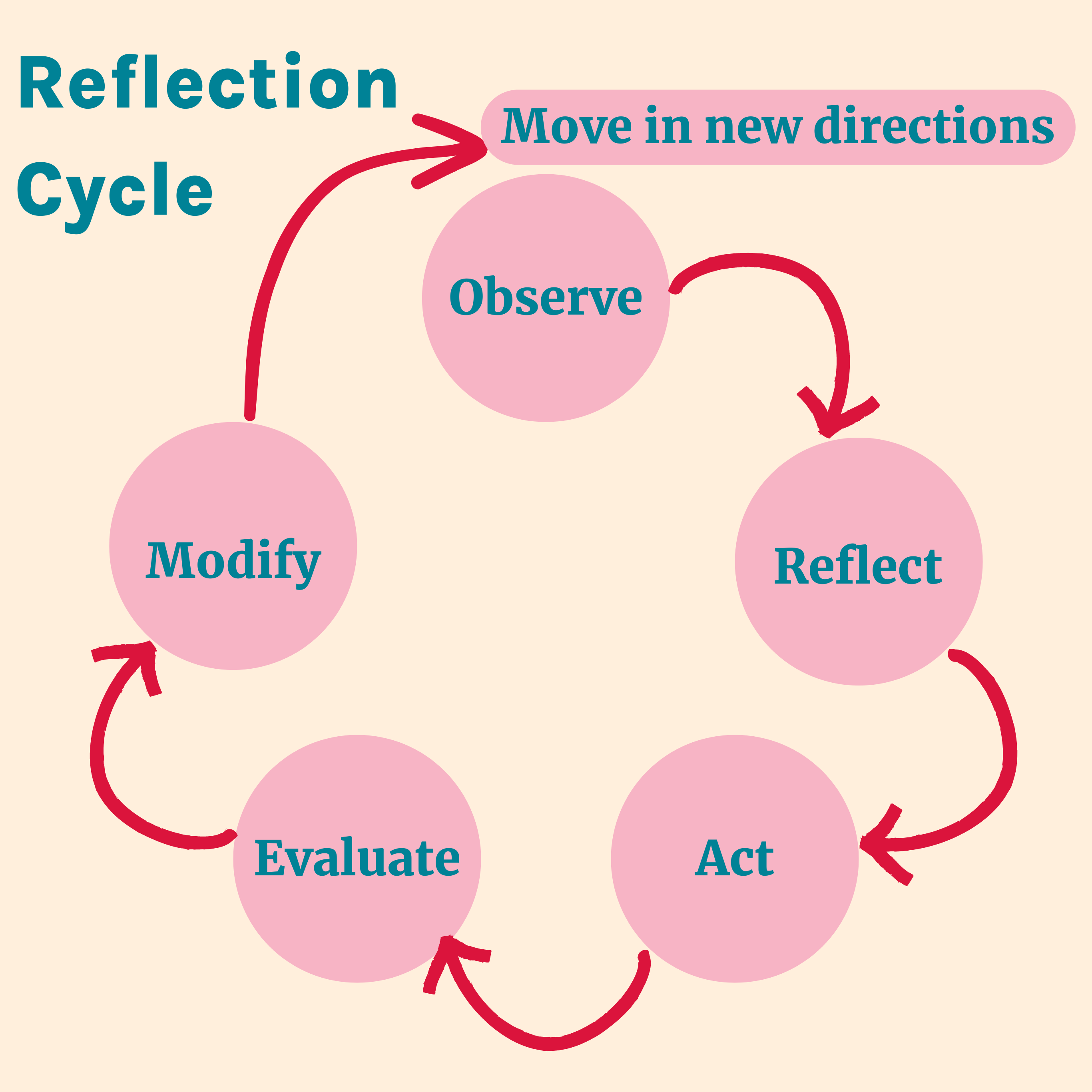
The McNiff Action Reflection Cycle promotes moving in new directions by building upon investigation and observations to reach new actions.2
The steps include:2
- Observing what's going on
- Identifying a concern
- Reflecting to move forward with a given concern
- Taking action to try out a new way
- Evaluating data about what's happening, and
- Modifying the plan as a result of what's discovered.
A 5 step reflection cycle. The background is cream with pink circles and boxes and red arrows.
Heading reads: reflection cycle
First line reads: move in new directions
Second line reads: observe
Third line reads: modify, reflect
Fourth line reads: evaluate, act
Reflective practice can be done on your own, with a supervisor, with co-workers, or within a A group of people who share a concern or a passion for something. They meet regularly to discuss the topic and learn more about it and how to improve.community of practice (CoP).
Reflective practice could look like:
- Keeping a journal or log of your work
- Engaging in formal and structured discussions with your supervisor or peers
- Engaging in informal and when something happens as necessary or needed.ad-hoc discussions with your supervisor or peers
- Discussing case studies in a CoP
- Using specific reflective and decision-making frameworks in your work
- Mind mapping
- Creative work like making music, art, videos, or creative writing to explore reflections
- Education and training in areas relevant to your work and linking lessons to your experiences
- Seeking feedback from employers
- Learning from experience and changing your approach, behaviour and practice based on your reflections
- Hall, J. (1 October 2018). Let’s Talk About Reflective Practice. https://ultimateyouthworker.com.au/2018/10/lets-talk-about-reflective-practice/
- Herman, M. (2012). Reflective Practice Meets Youth Work Supervision. https://www.youthandpolicy.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/herman_reflective_practice_meets_youth_work_supervision.pdf
Olivia and Nick have a conversation about the assumptions we make and how when we realise we have made a mistake, we feel uncomfortable. They ask us to embrace the discomfort and use it to motivate us to learn. Together they discuss why Person-first vs. Identity-first language is important to be aware of, how we can learn from our mistakes, challenge our own prejudices, and how we can apologise and take accountability.





